What is Wattle?
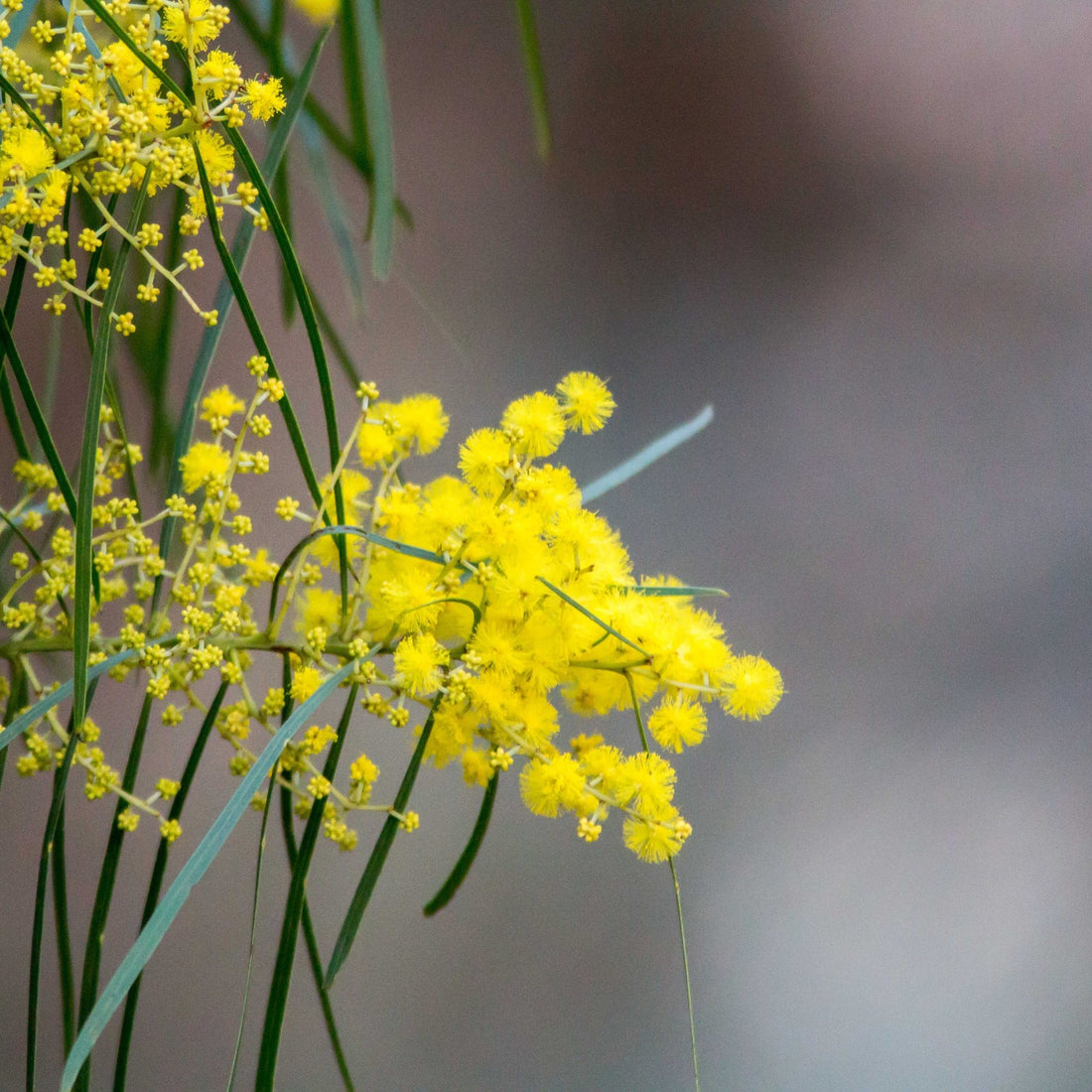
Wattle is a term used to describe a group of trees and shrubs that belong to the genus Acacia in the family Fabaceae. These plants are native to Australia and are known for their bright yellow or golden flowers that bloom in the spring or early summer. Wattle plants are hardy, fast-growing, and drought-tolerant, making them a popular choice for landscaping and gardening in Australia and other parts of the world. They can also be found in different shapes and sizes, from small shrubs to large trees.
Wattle, also known as Acacia, has a long history of use by Indigenous Australians. The bark, leaves, and seeds were used for a variety of purposes, including medicinal remedies, dyes, and food. The wood was also used to make tools and weapons.
Wattle plants were first described by European settlers in the late 18th century. They were initially used for practical purposes such as fencing and as a source of tannin for the leather industry. Over time, they became popular in ornamental horticulture and gardening, with many cultivars and hybrids being developed for use in landscaping.
Today, wattle is considered an iconic symbol of Australia, and it is celebrated annually on Wattle Day, which is held on the first day of September. The day is marked by the planting of new wattles, and the blooming of the golden flowers that symbolize the start of spring.
Wattle, or Acacia, is a diverse group of plants that includes over 1,000 species. They are known for their bright yellow or golden flowers that bloom in the spring or early summer. The leaves of wattle plants are typically small and feathery, and the branches are often twisted or gnarled.
Wattle plants are known for their hardiness and fast-growing nature. They are also drought-tolerant and can thrive in a range of soil types and conditions. This makes them a popular choice for landscaping and gardening, particularly in dry and arid regions.
In addition to their ornamental value, wattle plants have a variety of uses. The wood is strong and durable, and is often used for fence posts, furniture, and flooring. The bark and leaves of some species contain tannins, which are used in the production of leather and other products. The seeds of some species are edible, and the nectar from the flowers is a valuable source of food for bees and other insects.
Wattles are also used for soil stabilization on mine sites, for example, for phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils.
Overall, wattle plants are a versatile and valuable addition to any landscape or garden, offering both beauty and practical benefits.
Wattle In The Landscape
Wattle plants are native to Australia and are found in a wide range of habitats and environments. Some species are found in rainforests, while others are found in deserts or on the coast. They have adapted to grow in a wide range of soil types, from sandy soils to heavy clay soils.
In terms of growth habits, wattle plants can vary greatly in size and shape. Some species are small shrubs that only grow to a few feet tall, while others can reach heights of over 100 feet and have a spreading canopy. Some species are evergreen, while others are deciduous. Some species have a single trunk, while others have multiple trunks or a spreading habit.
In terms of growth rate, wattles are known for being fast-growing. They can grow up to 2-3 meters per year under good conditions. They are also hardy and can tolerate a range of climatic conditions, from dry and hot to cool and wet. They are also tolerant of frost and fire.
Wattle plants also have a deep root system that allows them to access water and nutrients from deep in the soil, making them well adapted to survive in arid and semi-arid regions.
Overall, wattle plants are highly adaptable and can thrive in a wide range of environments, making them well suited to many different types of landscapes and gardens.
Cultural Significance
Wattle is an important plant in the culture of Indigenous Australians, with a long history of use for medicinal, spiritual, and practical purposes. The bark, leaves, and seeds were used for a variety of purposes, including medicinal remedies, dyes, and food. The wood was also used to make tools and weapons. Different species of wattle have different cultural significance for different Indigenous communities.
Wattle is also an iconic symbol of Australia, celebrated annually on Wattle Day, which is held on the first day of September. The day is marked by the planting of new wattles and the blooming of the golden flowers that symbolize the start of spring.
In addition to its cultural significance, wattle is also economically important, particularly in rural areas where it is used for land rehabilitation and as a source of honey and other products. Many species of wattle are also used for soil stabilization on mine sites and for phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils.
Overall, wattle holds a significant cultural and economic place in Australia, and its blooming serves as a reminder of the start of spring and the beauty of the native flora.
Planting Wattle In The Garden Or Landscape
Wattle, also known as acacia, is a type of tree or shrub that is native to Australia and Africa. It is known for its bright yellow or orange flowers and its ability to tolerate dry conditions. In landscaping and gardening, wattle can be used as a hedge, screen, or specimen plant. It can also be used for erosion control on slopes. Wattle can grow in a variety of soils and can tolerate both full sun and partial shade. However, it should be noted that some species of wattle can be invasive in certain areas, so it is important to choose a non-invasive variety for your specific location.
Types Of Wattle
There are many species of wattle, but some of the most common ones include:
-
Acacia baileyana: This species is native to Australia and is known for its delicate, fern-like leaves and yellow flowers. It can grow up to 15 feet tall and is often used as a hedge or screen plant.
-
Acacia dealbata: This species is also known as "silver wattle" or "blue wattle" and is native to Australia. It has silver-blue foliage and bright yellow flowers. It can grow up to 30 feet tall and is often used as a specimen plant.
-
Acacia melanoxylon: This species is native to Australia and is known for its dark, shiny leaves and yellow flowers. It can grow up to 100 feet tall and is often used as a hedge or screen plant.
-
Acacia pycnantha: This species is native to Australia and is known for its bright yellow flowers and green foliage. It can grow up to 30 feet tall and is often used as a specimen plant.
-
Acacia senegal: This species is native to Africa and is known for its yellow flowers and green foliage. It is often used for erosion control on slopes and for reforestation.
It's important to know that some of these species are invasive in some places, it would be best to research the specific species of wattle and whether it is non-invasive in your area before planting it.
Wattle As Bonsai
Shaping a wattle tree into a bonsai involves a process called "bonsai training." This process involves manipulating the growth and shape of the tree to create a miniature version of a mature tree. The process of shaping a wattle into a bonsai can take several years, and requires patience, skill, and a deep understanding of the tree's growth habits.
The first step in shaping a wattle into a bonsai is to select a young tree or cutting and plant it in a small pot with well-draining bonsai soil. The tree should be kept in a location with the right amount of light and moisture to promote healthy growth.
Once the tree has established roots, the process of training can begin. This involves pruning and shaping the branches and foliage of the tree to create a miniature version of a mature tree. This is done by selectively removing leaves, branches and other growth using pruning shears, bonsai scissors and wire.
The use of bonsai wire is a common practice in shaping the branches and trunks of the wattle. The wire is wrapped around the branches and trunk in the desired shape and left in place for several months. As the tree grows, the wire will bite into the bark and shape the branches and trunk into the desired shape. The wire should be checked regularly and adjusted or removed as needed.
Another important aspect of bonsai training is repotting. Wattle trees need to be repotted every 2-3 years, as they grow rapidly. This process involves removing the tree from its pot and trimming the roots, then replanting it in a slightly larger pot with fresh bonsai soil.
It's important to note that shaping a wattle into a bonsai is a long-term project that requires patience, skill, and a deep understanding of the tree's growth habits. It's also important to research the specific species of wattle and its bonsai potential before attempting to shape it into a bonsai.
Growing wattle as a bonsai can present some unique challenges and considerations.
One of the main challenges is that wattle trees are fast-growing, which can make it difficult to maintain a miniature size and shape. This means that regular pruning and shaping is required to keep the tree in its desired form.
Another challenge is that wattle trees have a tendency to produce long, thin branches which can be difficult to shape. This can be overcome by wiring and pruning the branches to encourage the growth of shorter, thicker branches.
Another consideration is that wattle trees are adapted to dry and arid conditions, which can make it difficult to provide the right amount of water and humidity for the bonsai. This can be overcome by selecting a species of wattle that is suited to the climate in which it will be grown and by providing appropriate watering and humidity.
It's also important to consider the aesthetic of the tree. Wattle trees often have a delicate, fern-like foliage and bright yellow or orange flowers, which can be difficult to incorporate into a bonsai design. Careful pruning and selective wiring can help to create a more compact, mature-looking tree.
Lastly, it's important to research the specific species of wattle and its bonsai potential before attempting to shape it into a bonsai. Not all species of wattle are suitable for bonsai and some may have different growth habits and needs.
In conclusion, growing wattle as a bonsai can be challenging but with the right care, attention and knowledge it's possible to shape a beautiful and unique bonsai tree.
Here are some tips for maintaining and caring for wattle bonsai:
-
Watering: Wattle bonsai trees should be watered regularly, but it's important to not over-water them as they are adapted to dry conditions. Allow the soil to dry out slightly before watering again.
-
Lighting: Wattle bonsai trees prefer full sun to partial shade, so it is important to provide them with the appropriate amount of light.
-
Fertilizing: Fertilize your wattle bonsai tree regularly with a balanced fertilizer during the growing season.
-
Pruning: Prune your wattle bonsai tree regularly to maintain its shape and size. This will also encourage the growth of shorter, thicker branches.
-
Wiring: Wiring can be used to shape the branches and trunk of your wattle bonsai tree. Make sure to check the wire regularly and adjust or remove it as needed to avoid damaging the tree.
-
Repotting: Repot your wattle bonsai tree every 2-3 years, or when the roots outgrow the pot. Make sure to use well-draining bonsai soil and a pot that is slightly larger than the previous one.
-
Pest and Disease control: Be vigilant for pests and diseases that might affect the health of your wattle bonsai tree, regular check-up and treatment is necessary.
-
Patience: Remember that growing a wattle bonsai tree takes time and patience, it's a long-term project. Be patient and enjoy the process of watching your bonsai tree grow and change over time.
It's important to do research on the specific species of wattle you have, as well as the bonsai care and training techniques that work best for that species, to ensure the best care for your bonsai tree.