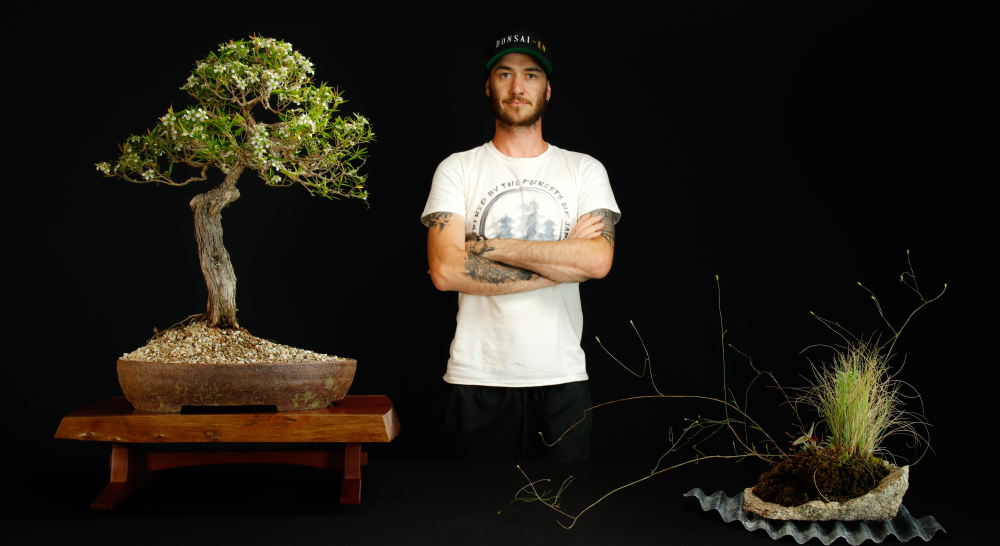
What is a Serissa?
Serissa, also known as snowrose or tree of a thousand stars, is a small shrub or tree in the family Rubiaceae. It is native to Southeast Asia and China, where it is commonly found growing in damp, shaded areas. The plant is known for its small, delicate leaves and small white or pink flowers that bloom in the spring or summer. The leaves are glossy and dark green, which are small and oval-shaped. The Serissa is a popular bonsai plant due to its small leaves, delicate flowers, and easy maintenance.
Serissa has small, glossy, dark green leaves that are oval-shaped and about 1-2 cm in length. The leaves are arranged alternately on the stem, giving the plant a delicate, lacy appearance. The plant produces small, white or pink flowers that bloom in the spring or summer. The flowers are star-shaped and have five petals. The overall growth habit of Serissa is a dense and compact, making it perfect for bonsai cultivation. It is a slow-growing plant, which makes it easy to maintain its small size and shape. Serissa is also a great option for indoor bonsai, as it can adapt to low light conditions and it is not demanding in terms of temperature.
Serissa is a small plant that typically grows to be around 2-3 feet tall, making it an ideal candidate for bonsai cultivation. The small size of its leaves, delicate flowers, and overall growth habit make it a popular choice among bonsai enthusiasts. Additionally, Serissa is relatively easy to maintain and shape, making it a suitable option for bonsai beginners. The ability to keep it small through pruning and wiring, and the fact that it can be grown indoors make it a great option for bonsai lovers.
Poplular types of serissa
There are several different types of Serissa, including:
-
Serissa foetida, also known as "tree of a thousand stars", is a small shrub with white, star-shaped flowers.
-
Serissa japonica, also known as "Japanese serissa", is a popular bonsai plant due to its small size and delicate leaves.
-
Serissa phoetida variegata, also known as "variegated serissa", is a cultivar of Serissa foetida that has variegated leaves with white or yellow edges.
-
Serissa Snowrose, also known as "Serissa foetida 'Snowrose'", is a popular variety of Serissa that has small, delicate white flowers and variegated leaves.
Native Environment
Serissa is native to tropical and subtropical regions of East Asia, specifically in China, Japan and Vietnam. It is commonly found growing in woodlands, forests, and along riverbanks.
Tips For Serissa As Bonsai
To maintain a Serissa bonsai, proper pruning and watering techniques should be used.
Pruning: Serissa should be pruned regularly to maintain its small size and shape. It is best to prune back to one or two leaves after each flush of growth. This will encourage the plant to produce smaller leaves and a denser branching structure. Wiring can also be used to shape the bonsai to the desired form. It is important to be careful not to damage the small leaves and branches when wiring.
Watering: Serissa bonsai should be kept consistently moist, but not waterlogged. It's best to water the bonsai when the soil surface feels dry to the touch. Overwatering can lead to leaf drop and yellowing leaves, while underwatering can cause the leaves to wilt and the branches to die back.
Light: Serissa bonsai prefers bright, indirect light. It can adapt to lower light conditions, but it will grow best in a location that receives bright, indirect light. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves. If grown indoors, a location near a north or east-facing window is ideal.
Fertilization: Feed the bonsai regularly with a balanced fertilizer during the growing season. Serissa can be sensitive to over-fertilization, so be sure to follow the manufacturer's instructions and use the fertilizer in the recommended amounts.
Temperature and Humidity: Serissa bonsai prefers temperatures between 15-30c (60-85°F), and a moderate level of humidity. It can tolerate a wide range of temperature and humidity conditions, but it will perform best in a warm and humid environment.
Common issues and solutions
When growing Serissa as a bonsai, some common problems that may be encountered include leaf drop and yellowing leaves. These issues can be caused by a variety of factors, including improper watering, fertilization, or light conditions.
Leaf drop: Leaf drop can be caused by a variety of factors, including underwatering or overwatering, high humidity, or exposure to direct sunlight. To prevent leaf drop, it is important to provide the bonsai with consistent moisture and bright, indirect light. Avoiding direct sunlight or keeping the bonsai in a location with high humidity can also help prevent leaf drop.
Yellowing leaves: Yellowing leaves can be a sign of over-fertilization, underwatering, or exposure to direct sunlight. To prevent yellowing leaves, it is important to fertilize the bonsai regularly but in the recommended amounts. Watering the bonsai consistently and providing bright, indirect light can also help prevent yellowing leaves. If the yellowing is extensive and accompanied by wilting, it may be a sign of a pest infestation, in which case it would be recommended to inspect the plant closely and apply an appropriate pesticide.
Other issues that can be encountered are pests and diseases, which can be controlled with appropriate pesticides and by avoiding overcrowding or poor ventilation.
It is important to keep an eye on the plant, and to address any issues that arise quickly, to prevent them from becoming severe and potentially damaging the bonsai.
To address leaf drop and yellowing leaves, the following suggestions may be helpful:
-
Proper fertilization: Feeding the bonsai regularly with a balanced fertilizer during the growing season can help prevent yellowing leaves caused by nutrient deficiencies. However, it is important to not over-fertilize the bonsai, as this can lead to yellowing leaves and other problems.
-
Consistent watering: Watering the bonsai consistently and keeping the soil consistently moist can help prevent leaf drop caused by underwatering or overwatering. Watering the bonsai when the soil surface feels dry to the touch is a good rule of thumb.
-
Bright, indirect light: Providing the bonsai with bright, indirect light can help prevent yellowing leaves and leaf drop caused by exposure to direct sunlight or low light conditions.
-
Pest control: To address pests or diseases, it is important to inspect the bonsai regularly for any signs of infestation. Common pests that can affect Serissa bonsai include spider mites, mealybugs and scale insects. If you notice any signs of infestation, it is important to address the problem quickly by applying an appropriate pesticide, following the manufacturer's instructions.
-
Proper humidity and temperature: Keeping the bonsai in an environment with moderate humidity and temperatures between 60-85°F can help prevent leaf drop and yellowing leaves caused by exposure to high humidity or extreme temperatures.
By following these suggestions, and by keeping an eye on the bonsai for any signs of stress or damage, you can help prevent leaf drop and yellowing leaves, and ensure that your Serissa bonsai stays healthy and beautiful.
As you can see serissa is a great plant for people to have in their gardens as a decorative plant or as a bonsai to enjoy the tiny flowers it produces.