What Is Camellia?
Camellia is a genus of evergreen shrubs or small trees that belongs to the family Theaceae. They are native to Asia, with China being the center of diversity for the species. Camellias are known for their large, showy flowers that bloom in the winter or early spring. They have glossy, dark green leaves and are often grown as ornamental plants in gardens and parks.
Camellias have been cultivated for centuries and have a rich history, especially in the Far East. They were first described by a Jesuit missionary in the 18th century and were later introduced to Europe and North America. Today, there are thousands of cultivars available, with a wide range of flower colors, sizes, and shapes.
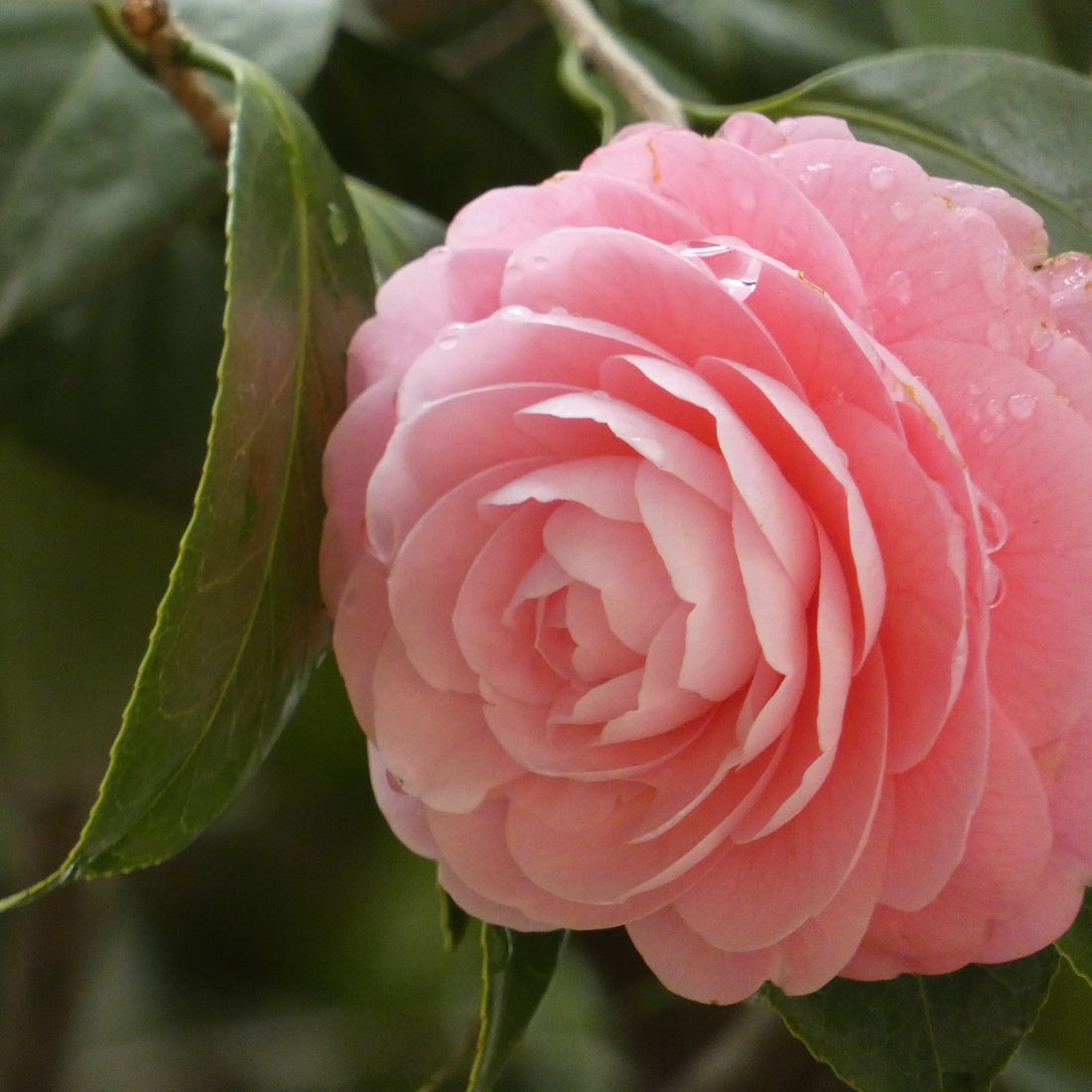
The flowers of camellia are usually large and conspicuous, generally white, pink, or red, and 2.5–4 cm in diameter. They are usually solitary or in small clusters, and come in a wide range of forms. The leaves are alternate, simple, glossy, and usually dark green, elliptic to oblong, 2–8 cm long and 1–3 cm broad, with a serrated margin.
Camellias are popular ornamental plants in parts of the world with temperate climates, including the southeastern United States, Japan, Korea, China, and Southeast Asia. They can be grown in a wide range of soils and are relatively low-maintenance, making them a great choice for gardeners of all skill levels.
Camellia is a genus of evergreen shrubs or small trees that belongs to the family Theaceae. The genus was named after the Jesuit missionary and botanist, Georg Kamel, who first described the plant in the late 17th century. Camellias are native to Asia, with China being the center of diversity for the species. They are believed to have originated in the mountains of China and are still widely cultivated there today.
The history of camellia dates back centuries, and the plant has played an important role in Asian culture. In China, the camellia has been revered for its beauty and elegance and has been depicted in art and literature for thousands of years. The Chinese have also used camellia oil for cooking and as a beauty aid for centuries.
In Japan, the camellia is also an important cultural symbol and is associated with the samurai class. The Japanese have been growing camellias for over a thousand years and have developed many cultivars with unique flower colors and shapes. In Japan, the camellia is also known as the "tsubaki" and is celebrated in festivals and competitions.
Camellias were first introduced to Europe and North America in the 18th century by European botanists and plant collectors. They were initially grown in botanical gardens and were later introduced to the horticulture trade. Today, camellias are widely cultivated in many parts of the world with temperate climates, including the southeastern United States, Japan, Korea, China, and Southeast Asia.
Characteristics of Camellia
Camellias are evergreen shrubs or small trees that typically grow to 3-6 meters tall, but can reach up to 30 meters tall in the wild. They have a dense and compact growth habit, with glossy, dark green leaves that are elliptic to oblong in shape. The leaves are usually 2-8 cm long and 1-3 cm broad, with a serrated margin.
The flowers of camellia are the plant's most striking feature. They are large and conspicuous, generally white, pink, or red, and 2.5–4 cm in diameter. They are usually solitary or in small clusters, and come in a wide range of forms. Some cultivars have single flowers, while others have semi-double or fully double flowers with many petals. The flowers are usually fragrant and bloom in the winter or early spring.
After the flowers have bloomed, camellias produce small, round, and glossy fruit that contain small seeds. The fruit is not edible and is typically discarded.
Camellias are also known for their glossy, dark green leaves and showy flowers, which bloom in the winter or early spring. They are relatively low-maintenance, making them a great choice for gardeners of all skill levels. The leaves are alternate, simple, glossy, and usually dark green, elliptic to oblong, 2–8 cm long and 1–3 cm broad, with a serrated margin.
Camellias are known for the wide variety of colors and shapes of their flowers. The most common flower colors are white, pink, and red, but other colors such as yellow, orange, and even purple can also be found in certain cultivars. The color of the flower can range from pure white to deep red and many shades in between. Some cultivars have variegated flowers with different colors on the same plant.
The shapes of the flowers also vary greatly among cultivars. Some cultivars have single flowers, which have only one row of petals. Others have semi-double flowers, which have a few extra rows of petals, and fully double flowers, which have many rows of petals and can look like a ball of petals. The flowers can be large, small, formal, or informal, and can be flat or have a ruffled shape.
Camellias are also known for their diversity in flower size, some cultivars have large flowers, while others have small flowers. Some cultivars have flowers with a diameter of up to 10 cm, while others have flowers with a diameter of only 2 cm.
The diversity in color, shape and size of Camellia flowers make them a popular plant among gardeners and horticulturists. The wide range of cultivars available means that there is a camellia to suit every taste and garden style.
Camellias are relatively hardy plants that can tolerate a wide range of growing conditions. They are best suited to areas with mild, humid climates and prefer cool temperatures and high humidity. They can tolerate light frosts but are not tolerant of prolonged freezing temperatures.
Soil: Camellias prefer well-draining, acidic soils with a pH between 5.5 and 6.5. They can tolerate a wide range of soil types, including clay, loam, and sandy soils, but prefer soils that are rich in organic matter.
Light: Camellias prefer bright, indirect light and should be protected from direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves. They will grow well in partial shade, but may not flower as heavily.
Water: Camellias prefer to be kept consistently moist, but not waterlogged. They should be watered regularly, especially during dry periods, to ensure that the soil remains consistently moist. They are sensitive to dry air, so it is important to keep the air around the plant humid, especially during the winter months.
Temperature: Camellias prefer cool temperatures, ideally between 10 and 20 °C. They can tolerate temperatures as low as -5 °C, but are not tolerant of prolonged freezing temperatures. They should be protected from hot summer sun and high temperatures, which can cause leaf burn and reduce flower production.
Fertilizer: Camellias respond well to fertilization and should be fertilized regularly during the growing season with an acid-based fertilizer. They should be fertilized before and after blooming to promote healthy growth and abundant flowers.
Popular Varieties of Camellia
There are thousands of cultivars of Camellia, and many are popular among gardeners and horticulturists. Here are a few popular varieties:
-
Camellia japonica: This is the most common and widely cultivated species of camellia. It has large, showy flowers that bloom in shades of pink, red, and white. The flowers are usually semi-double or fully double, and the plant can grow to be quite large. Some popular cultivars of Camellia japonica include 'Debutante', 'Donation', and 'Mathotiana Alba'.
-
Camellia sasanqua: This species of camellia is native to Japan and has smaller, more delicate flowers than Camellia japonica. The flowers are usually single and bloom in shades of pink, red, and white. The plant is smaller and more compact than Camellia japonica, making it a great choice for smaller gardens. Some popular cultivars of Camellia sasanqua include 'Bonanza', 'Cleopatra', and 'Yuletide'.
-
Camellia reticulata: This species is native to China and has large, showy flowers that bloom in shades of red and pink. The flowers are usually single and the plant is medium-sized. Some popular cultivars of Camellia reticulata include 'Crimson King', 'Early Pearly', and 'Golden Lanterns'.
-
Camellia sinensis: This species is the source of tea leaves, Camellia sinensis is a small to medium-sized evergreen shrub. The leaves are used to produce tea, and the plant can be grown in a variety of forms, including as a shrub, a standard, or a bonsai.
-
Camellia x williamsii: This is a hybrid species that is a cross between Camellia japonica and Camellia sasanqua. It has large, showy flowers that bloom in shades of pink, red, and white. The flowers are usually semi-double or fully double, and the plant is a medium-sized. Some popular cultivars of Camellia x williamsii include 'Adolphe Audusson', 'Crimson Glory', and 'Debbie'.
These are just a few of the many popular varieties of Camellia, and many others are available. The best variety for you will depend on your growing conditions, the space you have available, and your personal preferences.
Cultivation And Care
Camellias prefer well-draining, acidic soils with a pH between 5.5 and 6.5. They can tolerate a wide range of soil types, including clay, loam, and sandy soils, but prefer soils that are rich in organic matter. It's essential to prepare the soil well before planting Camellias, adding organic matter such as well-rotted manure or compost, to improve the soil structure and fertility.
Watering is an important aspect of Camellia care. They prefer to be kept consistently moist, but not waterlogged. They should be watered regularly, especially during dry periods, to ensure that the soil remains consistently moist. They are sensitive to dry air, so it's important to keep the air around the plant humid, especially during the winter months. A good way to do this is by placing a layer of mulch around the base of the plant to help retain moisture in the soil.
It's important to avoid over-watering Camellias, as this can lead to root rot and other problems. To check if your Camellia needs water, stick your finger in the soil about 2 inches deep, if the soil is dry, it's time to water. A general rule of thumb is to water deeply once a week, but this may vary depending on your climate and soil conditions.
During the winter months, it's essential to keep Camellias slightly drier, as the plant goes into a dormant phase, and the roots are less active during this time. It's also important to note that Camellias don't like to be waterlogged, so make sure that the soil is well-drained, and that water doesn't collect around the base of the plant.
Overall, Camellias are not demanding plants when it comes to soil and watering, but providing the right amount of water and the right soil conditions are essential for their growth and blooming.
Pruning and shaping are important aspects of Camellia care to maintain the plant's shape, promote healthy growth, and encourage the production of flowers. Camellias can be pruned to control their size, shape, and to encourage bushier growth.
Camellias can be pruned at any time of the year, but the best time to do it is after the plant has finished flowering. This way, you won't be cutting off any potential flowers. When pruning, it's important to use sharp, clean pruning shears to avoid damaging the plant.
Here are some tips for pruning and shaping Camellias:
- Remove any dead, diseased, or damaged wood. Cut back to healthy wood.
- Remove any shoots that are growing from the base of the plant. These shoots will not produce flowers and will only take energy away from the plant.
- Remove any suckers that are growing from the base of the plant.
- Thin out the plant by removing some of the older branches. This will allow light and air to reach the center of the plant and encourage bushier growth.
- Remove any branches that are crossing over each other or rubbing against each other.
- If you want to control the size of the plant, cut back the main branches by about a third.
- If you want to shape the plant, cut back the main branches to the desired shape.
It's important not to over-prune Camellias, as this can lead to a reduction in flower production. A light pruning each year is usually sufficient to keep the plant healthy and encourage bushier growth.
In addition to pruning, Camellias can also be shaped by training the branches to grow in a certain direction. This can be done by tying the branches to a support and adjusting the tie as the plant grows.
In summary, Pruning and shaping are important steps to maintain the health and beauty of Camellia, it helps to control the size, shape, and encourages bushier growth and more flowers. It's essential to use sharp, clean pruning shears and not to over-prune to avoid damaging the plant.
Pests And Disease
Camellias are generally hardy plants that are resistant to most pests and diseases. However, like all plants, they are susceptible to certain problems that can affect their growth and overall health. Here are some common pests and diseases that can affect Camellias:
-
Aphids: These small insects feed on the sap of Camellia leaves and can cause the leaves to curl and become distorted. They can also leave a sticky residue on the leaves, which can attract other pests.
-
Scale insects: These small insects attach themselves to the stems and leaves of Camellias and suck the sap, causing the leaves to yellow and the plant to become stunted.
-
Mealybugs: These small insects feed on the sap of Camellia leaves and can cause the leaves to turn yellow and the plant to become stunted.
-
Spider mites: These small insects feed on the sap of Camellia leaves and can cause the leaves to turn yellow and the plant to become stunted.
-
Camellia petal blight: This fungal disease causes the petals of Camellia flowers to turn brown and die. It is most common in humid conditions.
- Camellia leaf gall: This is a fungal disease that causes the leaves of Camellias to become thickened and distorted.
-
Root rot: This is a fungal disease that can occur if Camellias are planted in poorly-drained soil. The roots of the plant will become soft and black, and the plant will become stunted.
To prevent pests and diseases, it's essential to keep your Camellia healthy by providing the right growing conditions, including proper soil, water, light, and temperature. Regularly inspecting the plant and removing any infected leaves or branches can also help prevent the spread of pests and diseases. Applying a pesticide or fungicide may be necessary if an infestation is severe, but it's essential to follow the instructions and use it carefully.
In summary, Camellias are generally hardy plants that are resistant to most pests and diseases, but they can be affected by some common pests and diseases. To prevent these problems, it's essential to keep your Camellia healthy by providing the right growing conditions, regular inspection, and if necessary applying pesticide or fungicide with care.
Camellia As Bonsai
Camellia, also known as "Tsubaki" in Japanese, is a popular choice for bonsai. Bonsai is the art of creating miniature versions of trees and shrubs by growing them in small containers and pruning them to control their size and shape. Camellia is particularly well-suited for bonsai because of its natural beauty and its ability to be trained and shaped.
When grown as a bonsai, Camellias are usually kept small, with a height of around 20-30 cm, and trained to have a small, compact shape. They are often pruned to have a single trunk and a curved, natural shape.
The key to growing a Camellia bonsai is to provide the right growing conditions. Camellias prefer well-draining, acidic soils with a pH between 5.5 and 6.5, and they should be kept consistently moist but not waterlogged. They prefer bright, indirect light and should be protected from direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves. They also prefer cool temperatures, ideally between 10 and 20 °C.
Camellias are also known for their beautiful, showy flowers, which can be an important feature of a bonsai. The flowers can be white, pink, or red, and they usually bloom in the winter or early spring. To encourage blooming, Camellia bonsai should be fertilized regularly with an acid-based fertilizer, and they should be pruned and shaped to promote healthy growth and abundant flowers.
In summary, Camellia is a popular choice for bonsai, particularly for its natural beauty, ability to be trained and shaped, and for its showy flowers
Here are some tips and tricks for growing Camellia as bonsai:
-
Choose the right variety: Camellia japonica and Camellia sasanqua are the most commonly used varieties for bonsai. These varieties have smaller leaves and a more compact growth habit than other Camellia species, making them ideal for bonsai.
-
Provide the right soil: Camellias prefer well-draining, acidic soils with a pH between 5.5 and 6.5. They should be planted in a well-draining bonsai soil mix that contains a high proportion of organic matter, such as peat moss or compost.
-
Watering: Camellias like to be kept consistently moist, but not waterlogged. They should be watered regularly, especially during dry periods, to ensure that the soil remains consistently moist. Be sure to check the soil moisture regularly, as over-watering can lead to root rot.
-
Light: Camellias prefer bright, indirect light and should be protected from direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves. They will grow well in partial shade, but may not flower as heavily.
-
Temperature: Camellias prefer cool temperatures, ideally between 10 and 20 °C. They should be protected from hot summer sun and high temperatures, which can cause leaf burn