What Is bougainvillea?
Bougainvillea, also known as "Paperflower" or "Bugambilia", is a tropical and subtropical vine known for its vibrant, colorful bracts. These bracts, which can be pink, purple, red, orange, and yellow, are often mistaken for the plant's flowers. The true flowers of Bougainvillea are small and white, but they are usually hidden by the showy bracts.
Bougainvillea is native to South America but is now widely grown as an ornamental plant in many parts of the world, including the United States, Europe, and Asia. It is a popular choice for gardens, trellises, and fences, and can also be trained as a bonsai or grown in containers.
Bougainvillea is a hardy plant that is easy to care for, but it does require proper sunlight, irrigation, and fertilization to thrive. The plant is drought-tolerant and can be tolerant of salt spray, making it a great choice for coastal regions. With proper care, Bougainvillea will bloom year-round and can add a burst of color to any landscape.
Interesting Facts About The Plant
- Bougainvillea is named after French explorer Louis Antoine de Bougainville, who discovered the plant in South America in the 18th century.
- The bracts of the plant are not actually flowers, but modified leaves that surround the small, white true flowers.
- Bougainvillea is a drought-tolerant plant and can survive on very little water, making it a great choice for xeriscaping.
- The plant is known for its fast growth and can reach heights of up to 30 feet if left untrained.
- Bougainvillea is a popular choice for bonsai enthusiasts and can be trained into a variety of shapes and styles.
- The plant is known for its resistance to pests and diseases, making it a low-maintenance choice for gardeners.
- Some species of Bougainvillea have thorny stems, making them a popular choice for garden walls and fences.
- Bougainvillea is a popular choice for hanging baskets, as the cascading stems can create a striking display of color.
- The plant is also known for its long lasting flowers, as its bracts can stay on the plant for several weeks or even months.
10.Bougainvillea is not just limited to gardens, it also used in landscaping, as a hedge, or trained to grow over an arbor or pergola.
Types Of Bougainvilliea
- Bougainvillea glabra: This variety is also known as "Paperflower" and is known for its small, white flowers that are surrounded by large, papery bracts in shades of pink, purple, or red. It is a vigorous grower that can reach heights of up to 30 feet if left untrained.
- Bougainvillea spectabilis: This is one of the most popular varieties, known for its large, showy bracts that can be pink, purple, red, orange, or yellow. It is a vigorous grower that can reach heights of up to 40 feet if left untrained.
- Bougainvillea x buttiana: A hybrid of B.glabra and B.spectabilis, this variety is known for its large, colorful bracts and fast growth. It can reach heights of up to 30 feet if left untrained.
- Bougainvillea ‘San Diego Red’: This variety is known for its bright red bracts and compact growth habit, making it a great choice for small gardens or containers.
- Bougainvillea ‘Hawaii’: This variety is known for its large, pink bracts and compact growth habit, it is a popular choice for hanging baskets and as a houseplant.
- Bougainvillea ‘Singapore Pink’: This variety is known for its soft pink bracts and compact growth habit, it is a popular choice for small gardens and as a houseplant.
- Bougainvillea ‘Orange King’: This variety is known for its bright orange bracts and vigorous growth habit, it is a popular choice for large gardens or as a hedge.
Note: This is not an exhaustive list of varieties, there are many other cultivars available in different colors, shapes and sizes.
Cultivation and Care
Soil : Bougainvillea prefers well-draining, sandy or loamy soil with a slightly acidic to neutral pH of 6.0 to 7.0. It does not tolerate heavy clay soils. The plant prefers a soil that is moist but not waterlogged. To improve drainage and aeration, you can add perlite, sand, or coarse gravel to the soil.
Bougainvillea also prefer a soil that is rich in organic matter. You can add compost or well-rotted manure to the soil before planting. In addition, the plant may benefit from a slow-release fertilizer that is high in phosphorous and potassium, as these nutrients encourage blooming.
It's worth noting that bougainvillea are tough plants and can adapt to different soil types, but for optimal growth and flowering, it's best to provide the ideal soil type.
Watering: Bougainvillea is a drought-tolerant plant, but it does require regular watering, especially during hot and dry weather. The plant prefers consistently moist soil, but not waterlogged. A good rule of thumb is to water the plant when the top inch of soil is dry.
During the growing season, the plant may need to be watered once or twice a week, depending on the weather and soil conditions if it is planted in the ground. As a bonsai the watering requirements can be up to once or twice a day during the peak of growing season due to the limited space in the bonsai pot. In the winter, when the plant is dormant, it will need less water. It's important to avoid over-watering, which can lead to root rot.
Fertilizing: Bougainvillea will benefit from a slow-release fertilizer that is high in phosphorous and potassium, as these nutrients encourage blooming. You can fertilize the plant once a month during the growing season, following the instructions on the fertilizer package.
It's important to not to over-fertilize, as this can lead to lush foliage growth but fewer flowers. Also, avoid fertilizing during the fall and winter, when the plant is dormant.
In addition, during the growing season it is a good practice to supplement with a liquid fertilizer high in potassium and phosphorous to promote blooming and maintain the overall health of the plant.
It's worth noting that, as with most plants, the specific watering and fertilizing needs of bougainvillea will vary depending on local weather conditions, the size of the plant, the type of soil, and the size of the container. Keep an eye on the plant and adjust watering and fertilizing as needed.
Light: Bougainvillea is a tropical plant that prefers full sun, at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day is ideal for optimal growth and flowering. If grown indoors, it is important to place the plant near a sunny window or under grow lights.
Temperature: Bougainvillea is a tropical plant that prefers warm temperatures and can tolerate heat well. It can be grown in USDA hardiness zones 9-11. It can also be grown as a houseplant, but it will need to be kept in a warm room with temperatures between 60-90°F.
In areas with colder climates, Bougainvillea can be grown as a container plant and brought indoors during the winter or grown as an annual. In these cases, it is important to protect the plant from frost and freezing temperatures.
It's worth noting that, while bougainvillea can tolerate a wide range of temperatures, it will not survive prolonged freezing temperatures. In cold weather, bring the container indoors or cover the plant with frost protection cloth.
Pruning: Bougainvillea is a vigorous grower and will benefit from regular pruning to control its size and shape. The best time to prune is after the plant has finished blooming, typically in late winter or early spring.
For established plants, you can prune back the tips of the branches to control the size and shape of the plant. You can also remove any dead, diseased, or damaged wood. For a bushier plant, you can also pinch back the tips of the branches to encourage branching.
For bonsai, prune the plant regularly to maintain the desired shape, removing any unwanted branches or leaves.
Training: Bougainvillea can be trained to grow over a trellis, fence, or arbor, or as a standard tree. To train the plant, tie the branches to the support and gently guide them in the desired direction.
For bonsai, you can use wire to shape the branches and trunk of the plant, but be sure to check the wire regularly and remove it before it cuts into the bark.
It's worth noting that, as with most plants, the specific pruning and training needs of bougainvillea will vary depending on the size and shape of the plant, and the desired final form. Be patient and expect to prune and train the plant regularly to maintain its shape and size.
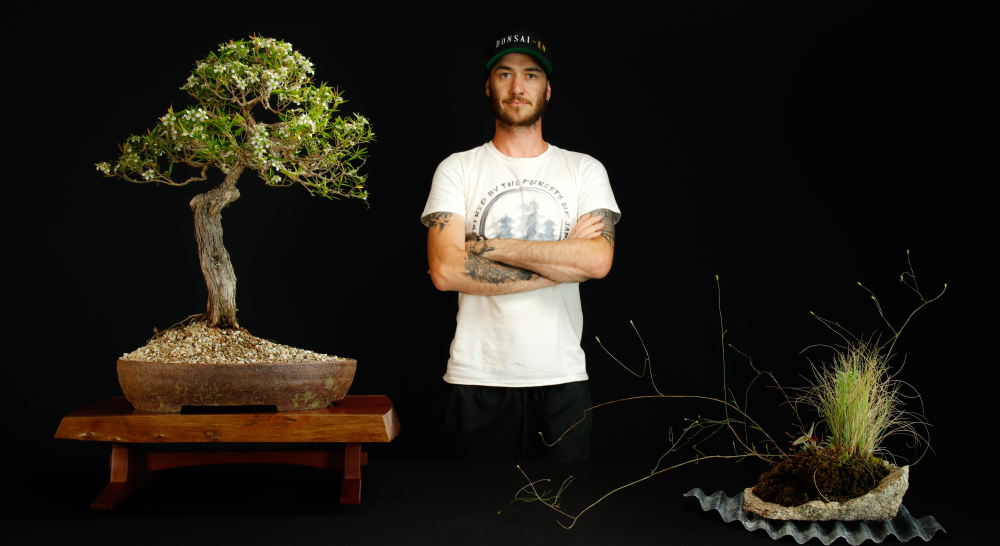
Bougainvillea As Bonsai
A Bougainvillea bonsai is a miniature version of the tropical vine, trained to grow in a small container with a specific shape and style. The bonsai form of Bougainvillea is characterized by its small size, well-proportioned branches, and a trunk that is thick at the base and tapers towards the top.
The bracts of the bonsai are usually smaller than those of the full-size plant, but they still provide a burst of color to the miniature landscape. The small leaves of the bonsai are typically green, and the small white flowers are often hidden by the bracts.
The bonsai form of Bougainvillea can be trained into a variety of shapes, such as the traditional informal upright, slanting, or cascade style. As a bonsai, Bougainvillea can be trained to have a small and compact size, and with proper care, it can bloom year-round, providing a beautiful display of color.
It's worth noting that training a bonsai is a process that requires patience, and it is important to use the right techniques and tools to achieve the desired form while keeping the plant healthy.
How To Care For Bougainvillea Bonsai
Caring for a Bougainvillea bonsai involves providing the right combination of light, water, soil, temperature, and pruning. Here are a few tips on how to care for a Bougainvillea bonsai:
- Light: Bougainvillea bonsai prefers full sun, at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day is ideal for optimal growth and flowering. If grown indoors, place the bonsai near a sunny window or under grow lights.
- Water: Bougainvillea bonsai prefers consistently moist soil, but not waterlogged. Water the bonsai when the top inch of soil is dry. Be careful not to over-water, which can lead to root rot.
- Soil: Bougainvillea bonsai prefers well-draining, sandy or loamy soil with a slightly acidic to neutral pH of 6.0 to 7.0. It does not tolerate heavy clay soils. Be sure to use a well-draining soil mix and make sure that the bonsai is planted in a container with drainage holes.
- Temperature: Bougainvillea bonsai prefers warm temperatures, and it can tolerate heat well. Keep the bonsai well watered during the hottest months to keep it healthy.
- Fertilizing: Fertilize the bonsai once a month during the growing season with a slow-release fertilizer that is high in phosphorous and potassium, as these nutrients encourage blooming.
- Pruning: Prune the bonsai regularly to maintain its shape and size. The best time to prune is after the plant has finished blooming, typically in late winter or early spring. Be sure to use the right techniques and tools to achieve the desired form while keeping the plant healthy.
- Wiring: You can use wire to shape the branches and trunk of the bonsai, but be sure to check the wire regularly and remove it before it cuts into the bark.
It's worth noting that the specific care needs of a Bougainvillea bonsai will vary depending on the local weather conditions, the size of the plant, the type of soil, and the size of the container. Keep an eye on the plant and adjust watering and fertilizing as needed.
Training And Shaping Techniques
Training and shaping a Bougainvillea bonsai involves guiding the growth of the plant to achieve a specific shape and style. Here are a few tips on training and shaping techniques for a Bougainvillea bonsai:
-
Wiring: Use copper or aluminum wire to shape the branches and trunk of the bonsai into the desired shape. Be sure to use the right size of wire for the branch and wrap it tightly but not too tightly to avoid damaging the bark. Check the wire regularly and remove it before it cuts into the bark.
-
Pruning: Prune the bonsai regularly to maintain its shape and size. The best time to prune is after the plant has finished blooming, typically in late winter or early spring. Be sure to use the right techniques and tools to achieve the desired form while keeping the plant healthy.
-
Defoliation: Removing the leaves from the bonsai can encourage the growth of new leaves and flowers. This technique can be used to create a smaller leaf size or to expose the trunk and branches. Be sure to do it carefully and only remove the leaves that are necessary for shaping the bonsai.
-
Repotting: Repotting the bonsai every 2-3 years can help to refresh the soil and promote new growth. Be sure to use a well-draining soil mix and a container with drainage holes.
-
Training styles: Bougainvillea bonsai can be trained into a variety of styles such as the traditional informal upright, slanting, or cascade. Choose a style that is appropriate for the shape and size of the bonsai and the desired final form.
It's worth noting that training and shaping a bonsai is a process that requires patience, and it is important to use the right techniques and tools to achieve the desired form while keeping the plant healthy. It is also important to be aware of the natural shape and habits of the plant, as well as its response to the pruning, wiring and other techniques used.
Common Problems and Solutions
Here are a few common issues and solutions for Bougainvillea bonsai:
-
Yellow leaves: Yellow leaves can be caused by over-watering, lack of sunlight, or lack of nutrients. Solution: Reduce watering, increase sunlight, or fertilize with a slow-release fertilizer high in phosphorous and potassium.
-
Lack of blooms: Lack of blooms can be caused by lack of sunlight, lack of nutrients, or improper pruning. Solution: Increase sunlight, fertilize with a slow-release fertilizer high in phosphorous and potassium, or prune the bonsai after it has finished blooming.
-
Wilting or drooping leaves: Wilting or drooping leaves can be caused by lack of water, over-watering, or pests. Solution: Check the soil moisture, reduce watering or increase watering, or inspect the bonsai for pests and treat accordingly.
-
Pests: Bougainvillea bonsai is prone to pests such as spider mites, mealybugs, and whiteflies. Solution: Use an insecticidal soap or pest oil to control pests.
-
Frost damage: Bougainvillea bonsai is not frost-tolerant and can be damaged by freezing temperatures. Solution: Bring the bonsai indoors or cover it with frost protection cloth during cold weather.
It's worth noting that, as with most plants, the specific issues and solutions for a Bougainvillea bonsai will vary depending on the local weather conditions, the size of the plant, the type of soil, and the size of the container. Keep an eye on the plant and address any issues as soon as they arise.
I hope this encourages you to give bougainvillea a go whether its in your garden or as a bonsai. The blooms will be rewarding!














1 comment
InLouisiana we have a long growing season, can defoliation be done more than once in a season. We are running 90+ degree days for long periods in summer. Are there any changes I should adopt for care and maintenance of my bougainvillea?